One thing to note a query execution does not go in parallel for all operators. It is decided per operator cost and your setting for 'Cost Threshold of Parallelism' and 'Max Degree of Parallelism'.
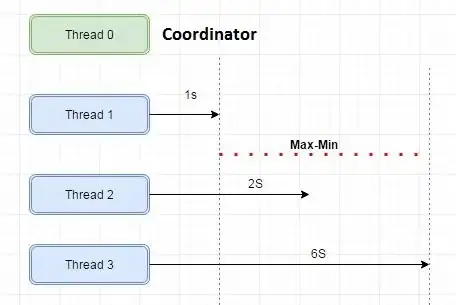
In theory you are looking at operations (operator with in execution plan) that had the highest delta in runtime between threads.
Depending on how much you collect, I suggest you create some indexes to speed things up. Let me know if you have any issues running my code.
/*============================================================================
PerThreadcollection.sql
Written by Taiob M Ali
SqlWorldWide.com
This script will show where queries (certain tasks within execution plan) are running
in parallel and difference in time for the longest thread and the shortest thread is high (excluding co-ordinator thread).
Instruction to run this script
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
--You will have to adjust @howManyTimes Variable values based on your requirements
--You will have to adjust @WaitSec Variable values based on your requirements
============================================================================*/
USE [DbaDB]
GO
--Creating table to hold raw data
SET ANSI_NULLS ON
GO
SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON
GO
CREATE TABLE [DbaDB].[dbo].[PerThreadcollection](
[timestamp] [datetime] NOT NULL,
[session_id] [smallint] NOT NULL,
[status] [nvarchar](30) NOT NULL,
[command] [nvarchar](32) NOT NULL,
[blocking_session_id] [smallint] NULL,
[wait_type] [nvarchar](60) NULL,
[exec_context_id] [int] NULL,
[task_state] [nvarchar](60) NULL,
[text] [nvarchar](max) NULL
) ON [PRIMARY]
GO
--Collecting raw data
DECLARE @howManyTimes int=0
DECLARE @WaitSec char(2) = '30'
DECLARE @Delay char(8)
SET @Delay = '00:' + '00:' +@WaitSec
WHILE(@howManyTimes<101)
BEGIN
INSERT INTO [DbaDB].[dbo].[PerThreadcollection]
SELECT
GETDATE(),
er.session_id,
er.status,
er.command,
er.blocking_session_id,
er.wait_type,
ot.exec_context_id,
ot.task_state,
st.text
FROM sys.dm_exec_requests er
JOIN sys.dm_os_tasks ot
ON ( er.session_id = ot.session_id )
CROSS apply sys.Dm_exec_sql_text(er.sql_handle) st
WHERE er.session_id IN (SELECT session_id
FROM sys.dm_os_tasks
GROUP BY session_id
HAVING Count(exec_context_id) > 1)
WAITFOR DELAY @Delay
SET @howManyTimes = @howManyTimes + 1
END
GO
;WITH MinExecution (sessionID, execContextId, queryText, mintime)
AS
(
Select session_id, exec_context_id, [text], MIN(timestamp) AS [MinTime]
FROM [DbaDB].[dbo].[PerThreadcollection]
WHERE exec_context_id <>0
GROUP BY session_id, exec_context_id, [text]
),
MaxExecution (sessionID, execContextId, queryText, maxtime)
AS
(
SELECT session_id, exec_context_id, [text], MAX(timestamp) AS [MaxTime]
FROM [DbaDB].[dbo].[PerThreadcollection]
WHERE exec_context_id <>0
GROUP BY session_id, exec_context_id, [text]
)
SELECT sessionId, queryText, (MAX(duration)-MIN(duration)) AS [deltaInSeconds] from
(
SELECT
mi.sessionID, mi.execContextId,mi.queryText ,DATEDIFF(ss, minTime, maxTime) AS [duration]
FROM MinExecution AS mi
JOIN MaxExecution AS mx
ON mi.sessionID=mx.sessionID
AND mi.execContextId=mx.execContextId
AND mi.queryText=mx.queryText) as t
GROUP BY sessionId, queryText
ORDER BY [deltaInSeconds] DESC
GO