I work with postgresql (and Postgis) for years now on a VM with dockers, and I start to be used to tweak servers parameters and optimize request, and I never had the kind of problems I have with Azure Postgresql.
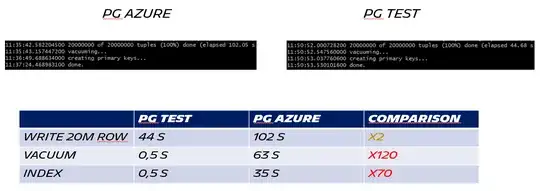
The problem is the following: writing is slow (usually around X2 compared to normal PG) but vacuum and index are EXTREMELY slow. At one point we need to create a PostGIS index on 500 millions row, on another server it takes around 30 minutes, on Azure instance it takes MORE THAN A DAY.
I tried to modify server parameters, checked the requests and finally went back to the basics to check the performance of the server, and I still don't understand if there is something I missed or if Azure Postgres has a big problem.
Here what I did to compare:
- Servers:
- PG TEST:
- basic docker postgres 11 hosted on a VM (SSD, enough ram and cores but it's not really relevant)
- command to launch:
docker run --rm -e POSTGRES_PASSWORD=pass -d postgres:11.14-stretch
- PG AZURE:
- azure database for postgresql, single server, memory optimized 8 cores, 1028Gb of storage
- default server parameters
- PG TEST:
- Test from local PC (I don't really care about response time):
- use pgbench and create a table with factor 50 (cmd:
pgbench -i -s 50) - look at the time to create the table, vacuum and index
- use pgbench and create a table with factor 50 (cmd:
This is the most simple and reproductible I could find. The exact result can vary a little, but it's around the same idea:
Read performance seems to be pretty good, so it's really a writing problem, and the more problematic one for us is index creation, and I don't see what can explain that.
This is a big problem for us, and I doubt that this is the kind of difference that can change with a few tweaks in the parameters, except if there is something specific to Azure ?
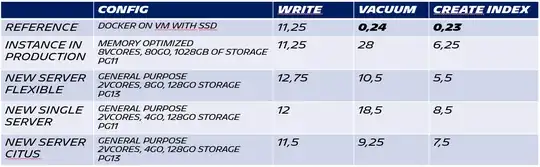
Did I miss something big ? Am I the only who have this kind of performance ? Or is it something limited to the system itself ? (I read that size of disk impact IOPS but looking at the graphs there doesn't seem to be a problem here, and we tried to add disk and it didn't change much) Maybe flexible servers doesn't have this issue ?
EDIT:
We tested to create new Azure postgres services with 3 different types of services (of the 4 possibles) that we just create and didn't modify, to be sure. I did the same test as before, 2 times for each service, and took the mean. I added the reference (called above PG TEST) and the one we have in production (called above PG AZURE). There was a few change with the previous results, and flexible server seems to be a bit better but the problem is still the same: