I'm encountering an issue in SQL Server 2019 when using SSMS (versions 20.2 and 21 preview). Navigating to a table and opening the "Properties" dialog consistently results in a timeout.
After some investigation, I discovered the problem stems from the underlying query executed by SSMS:
EXEC sp_executesql
N'
CREATE TABLE #tmp_extended_remote_data_archive_tables
(object_id int not null, remote_table_name nvarchar(128) null, filter_predicate nvarchar(max) null, migration_state tinyint null)
IF EXISTS(SELECT 1 FROM master.sys.syscolumns WHERE Name = N''remote_data_archive_migration_state'' AND ID = Object_ID(N''sys.tables''))
EXECUTE(N''INSERT INTO #tmp_extended_remote_data_archive_tables SELECT rdat.object_id, rdat.remote_table_name,
SUBSTRING(rdat.filter_predicate, 2, LEN(rdat.filter_predicate) - 2) as filter_predicate,
CASE
WHEN tbl.remote_data_archive_migration_state_desc = N''''PAUSED'''' THEN 1
WHEN tbl.remote_data_archive_migration_state_desc = N''''OUTBOUND'''' THEN 3
WHEN tbl.remote_data_archive_migration_state_desc = N''''INBOUND'''' THEN 4
WHEN tbl.remote_data_archive_migration_state_desc = N''''DISABLED'''' THEN 0
ELSE 0
END AS migration_state
FROM sys.tables tbl LEFT JOIN sys.remote_data_archive_tables rdat ON rdat.object_id = tbl.object_id
WHERE rdat.object_id IS NOT NULL'')
ELSE
EXECUTE(N''INSERT INTO #tmp_extended_remote_data_archive_tables SELECT rdat.object_id, rdat.remote_table_name,
SUBSTRING(rdat.filter_predicate, 2, LEN(rdat.filter_predicate) - 2) as filter_predicate,
CASE
WHEN rdat.is_migration_paused = 1 AND rdat.migration_direction_desc = N''''OUTBOUND'''' THEN 1
WHEN rdat.is_migration_paused = 1 AND rdat.migration_direction_desc = N''''INBOUND'''' THEN 2
WHEN rdat.is_migration_paused = 0 AND rdat.migration_direction_desc = N''''OUTBOUND'''' THEN 3
WHEN rdat.is_migration_paused = 0 AND rdat.migration_direction_desc = N''''INBOUND'''' THEN 4
ELSE 0
END AS migration_state
FROM sys.tables tbl LEFT JOIN sys.remote_data_archive_tables rdat ON rdat.object_id = tbl.object_id
WHERE rdat.object_id IS NOT NULL'')
SELECT
tbl.name AS [Name],
tbl.object_id AS [ID],
tbl.create_date AS [CreateDate],
tbl.modify_date AS [DateLastModified],
ISNULL(stbl.name, N'''') AS [Owner],
CAST(case when tbl.principal_id is null then 1 else 0 end AS bit) AS [IsSchemaOwned],
SCHEMA_NAME(tbl.schema_id) AS [Schema],
CAST(
case
when tbl.is_ms_shipped = 1 then 1
when (
select
major_id
from
sys.extended_properties
where
major_id = tbl.object_id and
minor_id = 0 and
class = 1 and
name = N''microsoft_database_tools_support'')
is not null then 1
else 0
end
AS bit) AS [IsSystemObject],
CAST(OBJECTPROPERTY(tbl.object_id, N''HasAfterTrigger'') AS bit) AS [HasAfterTrigger],
CAST(OBJECTPROPERTY(tbl.object_id, N''HasInsertTrigger'') AS bit) AS [HasInsertTrigger],
CAST(OBJECTPROPERTY(tbl.object_id, N''HasDeleteTrigger'') AS bit) AS [HasDeleteTrigger],
CAST(OBJECTPROPERTY(tbl.object_id, N''HasInsteadOfTrigger'') AS bit) AS [HasInsteadOfTrigger],
CAST(OBJECTPROPERTY(tbl.object_id, N''HasUpdateTrigger'') AS bit) AS [HasUpdateTrigger],
CAST(OBJECTPROPERTY(tbl.object_id, N''IsIndexed'') AS bit) AS [HasIndex],
CAST(OBJECTPROPERTY(tbl.object_id, N''IsIndexable'') AS bit) AS [IsIndexable],
CAST(CASE idx.index_id WHEN 1 THEN 1 ELSE 0 END AS bit) AS [HasClusteredIndex],
CAST(ISNULL((select top 1 1 from sys.indexes ind where ind.object_id = tbl.object_id and ind.type > 1 and ind.is_hypothetical = 0 ), 0) AS bit) AS [HasNonClusteredIndex],
CAST(case idx.index_id when 1 then case when (idx.is_primary_key + 2*idx.is_unique_constraint = 1) then 1 else 0 end else 0 end AS bit) AS [HasPrimaryClusteredIndex],
CAST(ISNULL((select top 1 1 from sys.indexes ind where ind.object_id = tbl.object_id and ind.type = 6 and ind.is_hypothetical = 0 ), 0) AS bit) AS [HasNonClusteredColumnStoreIndex],
CAST(ISNULL((select top 1 1 from sys.indexes ind where ind.object_id = tbl.object_id and ind.type = 3 and ind.is_hypothetical = 0 ), 0) AS bit) AS [HasXmlIndex],
CAST(CASE idx.type WHEN 0 THEN 1 ELSE 0 END AS bit) AS [HasHeapIndex],
CAST(ISNULL((select top 1 1 from sys.all_columns as clmns join sys.types as usrt on usrt.user_type_id = clmns.user_type_id where clmns.object_id = tbl.object_id and usrt.name = N''xml''), 0) AS bit) AS [HasXmlData],
CAST(ISNULL((select top 1 1 from sys.all_columns as clmns join sys.types as usrt on usrt.user_type_id = clmns.user_type_id where clmns.object_id = tbl.object_id and usrt.name in (N''geometry'', N''geography'')), 0) AS bit) AS [HasSpatialData],
tbl.uses_ansi_nulls AS [AnsiNullsStatus],
CAST(ISNULL(OBJECTPROPERTY(tbl.object_id,N''IsQuotedIdentOn''),0) AS bit) AS [QuotedIdentifierStatus],
CAST(0 AS bit) AS [FakeSystemTable],
ISNULL(dstext.name,N'''') AS [TextFileGroup],
CAST(tbl.is_memory_optimized AS bit) AS [IsMemoryOptimized],
case when (tbl.durability=1) then 0 else 1 end AS [Durability],
tbl.is_replicated AS [Replicated],
tbl.lock_escalation AS [LockEscalation],
CAST(case when ctt.object_id is null then 0 else 1 end AS bit) AS [ChangeTrackingEnabled],
CAST(ISNULL(ctt.is_track_columns_updated_on,0) AS bit) AS [TrackColumnsUpdatedEnabled],
tbl.is_filetable AS [IsFileTable],
ISNULL(ft.directory_name,N'''') AS [FileTableDirectoryName],
ISNULL(ft.filename_collation_name,N'''') AS [FileTableNameColumnCollation],
CAST(ISNULL(ft.is_enabled,0) AS bit) AS [FileTableNamespaceEnabled],
CASE WHEN ''PS''=dsidx.type THEN dsidx.name ELSE N'''' END AS [PartitionScheme],
CAST(CASE WHEN ''PS''=dsidx.type THEN 1 ELSE 0 END AS bit) AS [IsPartitioned],
CASE WHEN ''FD''=dstbl.type THEN dstbl.name ELSE N'''' END AS [FileStreamFileGroup],
CASE WHEN ''PS''=dstbl.type THEN dstbl.name ELSE N'''' END AS [FileStreamPartitionScheme],
CAST(CASE idx.type WHEN 5 THEN 1 ELSE 0 END AS bit) AS [HasClusteredColumnStoreIndex],
CAST(CASE tbl.temporal_type WHEN 2 THEN 1 ELSE 0 END AS bit) AS [IsSystemVersioned],
CAST(ISNULL(historyTable.name, N'''') AS sysname) AS [HistoryTableName],
CAST(ISNULL(SCHEMA_NAME(historyTable.schema_id), N'''') AS sysname) AS [HistoryTableSchema],
CAST(ISNULL(historyTable.object_id, 0) AS int) AS [HistoryTableID],
CAST(CASE WHEN periods.start_column_id IS NULL THEN 0 ELSE 1 END AS bit) AS [HasSystemTimePeriod],
CAST(
ISNULL((SELECT cols.name
FROM sys.columns cols
WHERE periods.object_id = tbl.object_id
AND cols.object_id = tbl.object_id
AND cols.column_id = periods.start_column_id), N'''')
AS sysname) AS [SystemTimePeriodStartColumn],
CAST(
ISNULL((SELECT cols.name
FROM sys.columns cols
WHERE periods.object_id = tbl.object_id
AND cols.object_id = tbl.object_id
AND cols.column_id = periods.end_column_id), N'''')
AS sysname) AS [SystemTimePeriodEndColumn],
tbl.temporal_type AS [TemporalType],
CAST(tbl.is_remote_data_archive_enabled AS bit) AS [RemoteDataArchiveEnabled],
CAST(
ISNULL(rdat.migration_state, 0)
AS tinyint) AS [RemoteDataArchiveDataMigrationState],
CAST(rdat.filter_predicate AS varchar(4000)) AS [RemoteDataArchiveFilterPredicate],
CAST(rdat.remote_table_name AS sysname) AS [RemoteTableName],
CAST(CASE WHEN rdat.remote_table_name IS NULL THEN 0 ELSE 1 END AS bit) AS [RemoteTableProvisioned],
CAST(tbl.is_external AS bit) AS [IsExternal],
CAST(tbl.is_node AS bit) AS [IsNode],
CAST(tbl.is_edge AS bit) AS [IsEdge]
FROM
sys.tables AS tbl
LEFT OUTER JOIN sys.database_principals AS stbl ON stbl.principal_id = ISNULL(tbl.principal_id, (OBJECTPROPERTY(tbl.object_id, ''OwnerId'')))
INNER JOIN sys.indexes AS idx ON
idx.object_id = tbl.object_id and (idx.index_id < @_msparam_0 or (tbl.is_memory_optimized = 1 and idx.index_id = (select min(index_id) from sys.indexes where object_id = tbl.object_id)))
LEFT OUTER JOIN sys.data_spaces AS dstext ON tbl.lob_data_space_id = dstext.data_space_id
LEFT OUTER JOIN sys.change_tracking_tables AS ctt ON ctt.object_id = tbl.object_id
LEFT OUTER JOIN sys.filetables AS ft ON ft.object_id = tbl.object_id
LEFT OUTER JOIN sys.data_spaces AS dsidx ON dsidx.data_space_id = idx.data_space_id
LEFT OUTER JOIN sys.tables AS t ON t.object_id = idx.object_id
LEFT OUTER JOIN sys.data_spaces AS dstbl ON dstbl.data_space_id = t.Filestream_data_space_id and (idx.index_id < 2 or (idx.type = 7 and idx.index_id < 3))
LEFT OUTER JOIN sys.tables as historyTable ON historyTable.object_id = tbl.history_table_id
LEFT OUTER JOIN sys.periods as periods ON periods.object_id = tbl.object_id
LEFT OUTER JOIN #tmp_extended_remote_data_archive_tables AS rdat ON rdat.object_id = tbl.object_id
WHERE
(tbl.name=@_msparam_1 and SCHEMA_NAME(tbl.schema_id)=@_msparam_2)
DROP TABLE #tmp_extended_remote_data_archive_tables
',
N'@_msparam_0 nvarchar(4000),@_msparam_1 nvarchar(4000),@_msparam_2 nvarchar(4000)',
@_msparam_0 = N'2',
@_msparam_1 = N'TABLENAME',
@_msparam_2 = N'SCHEMANAME';
This query takes a long time to execute, but removing the LEFT JOIN on sys.filetables (along with related columns) allows it to run almost instantly.
Is there a way to optimize or work around this behavior, or to fix this problem?
For context:
I have two filetables in the database. Each filetable contains less than 50 records.
I have found that running a SELECT * against either sys.tables or sys.filetables independently completes almost instantly, but running
SELECT *
from sys.tables as tbl
left join sys.filetables as ft on ft.object_id = tbl.object_id
takes 4 minutes for the execution to complete. Though I see the results begin to appear after a few seconds.
Example messages from an execution with statistics io on are below
(29926 row(s) affected)
Table 'sysschobjs'. Scan count 2, logical reads 50935755, physical reads 0, page server reads 0, read-ahead reads 0, page server read-ahead reads 0, lob logical reads 0, lob physical reads 0, lob page server reads 0, lob read-ahead reads 0, lob page server read-ahead reads 0.
Table 'Worktable'. Scan count 0, logical reads 0, physical reads 0, page server reads 0, read-ahead reads 0, page server read-ahead reads 0, lob logical reads 0, lob physical reads 0, lob page server reads 0, lob read-ahead reads 0, lob page server read-ahead reads 0.
Table 'sysmultiobjrefs'. Scan count 29926, logical reads 110051, physical reads 0, page server reads 0, read-ahead reads 0, page server read-ahead reads 0, lob logical reads 0, lob physical reads 0, lob page server reads 0, lob read-ahead reads 0, lob page server read-ahead reads 0.
Table 'sysidxstats'. Scan count 29926, logical reads 100408, physical reads 0, page server reads 0, read-ahead reads 0, page server read-ahead reads 0, lob logical reads 0, lob physical reads 0, lob page server reads 0, lob read-ahead reads 0, lob page server read-ahead reads 0.
Table 'Workfile'. Scan count 0, logical reads 0, physical reads 0, page server reads 0, read-ahead reads 0, page server read-ahead reads 0, lob logical reads 0, lob physical reads 0, lob page server reads 0, lob read-ahead reads 0, lob page server read-ahead reads 0.
Table 'Worktable'. Scan count 0, logical reads 0, physical reads 0, page server reads 0, read-ahead reads 523, page server read-ahead reads 0, lob logical reads 0, lob physical reads 0, lob page server reads 0, lob read-ahead reads 0, lob page server read-ahead reads 0.
Table 'syssingleobjrefs'. Scan count 5, logical reads 325, physical reads 0, page server reads 0, read-ahead reads 0, page server read-ahead reads 0, lob logical reads 0, lob physical reads 0, lob page server reads 0, lob read-ahead reads 0, lob page server read-ahead reads 0.
Table 'syspalnames'. Scan count 1, logical reads 2, physical reads 0, page server reads 0, read-ahead reads 0, page server read-ahead reads 0, lob logical reads 0, lob physical reads 0, lob page server reads 0, lob read-ahead reads 0, lob page server read-ahead reads 0.
Table 'syspalvalues'. Scan count 2, logical reads 4, physical reads 0, page server reads 0, read-ahead reads 0, page server read-ahead reads 0, lob logical reads 0, lob physical reads 0, lob page server reads 0, lob read-ahead reads 0, lob page server read-ahead read
I think the very high reads on 'sysschobjs' are a cause of this? That internal table has just under 67K rows.
(The actual execution plan for another run is here: https://www.brentozar.com/pastetheplan/?id=HJ0EXXAMyg)
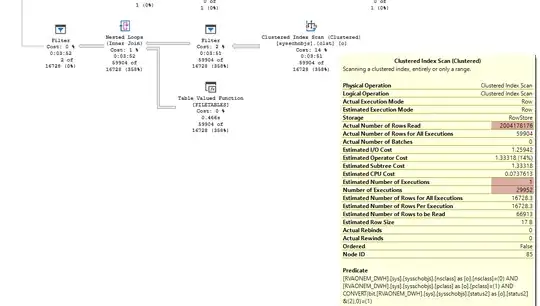
The slowest part of the execution plan is below. It estimates that it will scan sysschobjs once but in reality scans it 29952 times. Returning 2 rows per execution but reading 2,004,178,176 in aggregate across all of these scans.