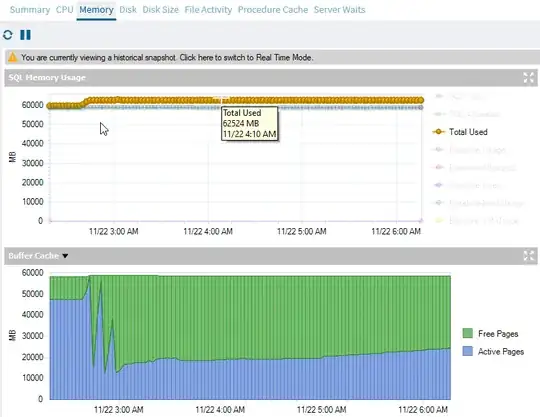
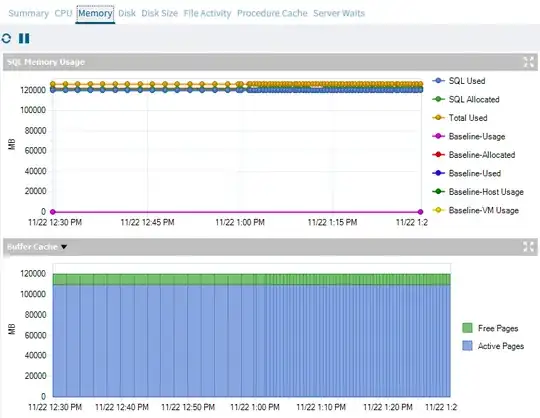
The buffer cache is a dedicated area in RAM to store data and index pages to prevent reading tables directly from disk. I believe the monitoring tool considers anything in the buffer cache to be USED memory, which includes both active and free pages.
According to Microsoft:
A page remains in the buffer cache until the buffer manager needs the buffer area to read in more data. Data is written back to disk only if it's modified. Data in the buffer cache can be modified multiple times before being written back to disk.
So, the buffer manager will cache data as long as possible and as much as possible until memory is needed for new stuff and there is no free space available.
--
As I noticed, the number of active pages spiked, with a few ups and downs until it stabilized at low values with gradual increase overtime.
The number of active pages was at high points due to memory pressure caused by some queries.
That caused the buffer manager to flush pages from the buffer cache back to disk, creating free pages.
A high number of free pages doesn't indicate if the memory usage is efficient but often associated with high memory pressure.
Subsequent workloads would cause SQL Server to load data from disk back into memory. Over time, the number of active pages slowly increased as the buffer filled the free pages with newly accessed data. If you give it enough time (depends on your workload), the buffer will fill up all the free pages with active pages eventually.
You may consider looking at the following charts to troubleshoot the issue:
Page Life Expectancy chart: Provides the time in seconds that a page remains in the cache or buffer pool. A significant drop indicates memory pressure. I often use this metric to identify when the issue started happening and checked resource-intensive queries running around that time.
Memory Area chart: Provides detailed insights into memory usage by components like Procedure Cache, Connections, Locks, Database, Optimizer, Sort, Hash, and Index.
Cache Hit Ratios: Displays the hit ratios of the Buffer and Procedure cache.
Also, queries with large memory grant can cause memory issue, you can check for those queries with high memory consumptions using Query Store or sp_BlitzCache from Brent Ozar - blitz.