I hope this question is easy for someone to answer :)
I have a table that looks like this (unimportant columns hidden)
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[Log](
[LogID] [int] IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL,
--several other columns
[Name] [nvarchar](512) NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT [PK_Log] PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED
(
[LogID] ASC
)WITH (PAD_INDEX = OFF, STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE = OFF, IGNORE_DUP_KEY = OFF, ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = ON, ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS = ON) ON [PRIMARY]
) ON [PRIMARY] TEXTIMAGE_ON [PRIMARY]
GO
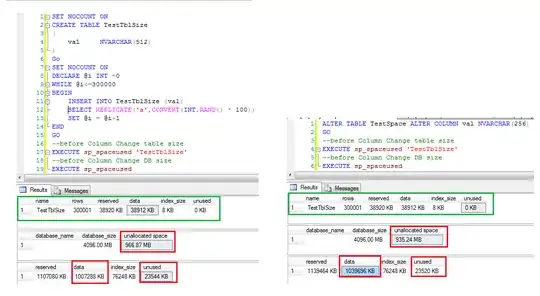
Now I did some indexing on that table and that also involved shortening the Name-column to 256 width.
But when I change this column
ALTER TABLE Log ALTER COLUMN Name NVARCHAR(256) NOT NULL
GO
The database grows by a non trivial amount. (And yes I double checked - this is the only change I make here) In total that table has 90746 entries and before altering the table SSMS said the size was 247.56MB.
But after this update the database grew to 336.13MB.
Don't know if that matters here but SELECT @@VERSION gets Microsoft SQL Server 2008 (SP1) - 10.0.2531.0 (X64)
Mar 29 2009 10:11:52
Copyright (c) 1988-2008 Microsoft Corporation
Express Edition (64-bit) on Windows NT 6.1 <X64> (Build 7601: Service Pack 1)
How can this be? Can someone explain?
UPDATE: I tried DBCC SHRINKDATABASE (myyDB, 0); that led to a smaller database of 268.81MB, but that is still bigger than the original database size with a wider column, I still do not understand :)