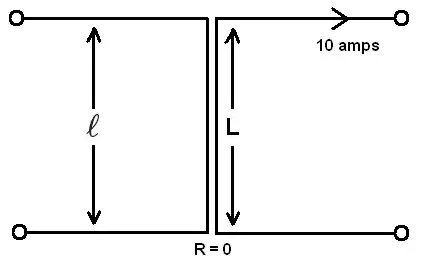
Calculate the magnetic rate of flux change induced by the conductor B between the distance R and infinity.
The emf induced in conductor A = N d(phi)/dt. Here N =1, because there is only a single wire. phi is the magnetic flux enclosed by the conductor A.
The current you have provided is 10 Amperes. This is an RMS value, I assume. The peak value, assuming it is a sine wave is = sqrt(2)*10 = 14.41 Amps.
The equation of the current flow in A = 14.41* sin(wt), where w = 2*pi*f *t, f is in HZ (or cycles per second). You have not specified the frequency. Also, the medium in which the conductors are situated. You have to account for the magnetic permeability of the medium.
Here is a python program that calculates the voltage between points 1 and 2:
"""
Python program to calculate the voltage induced in a wire
by another parallel wire, both of finite length.
The formula given above appears to be wrong.
It is possible for the self inductance.
What we need here is a formula for the MUTUAL inductance.
Formula for the mutual inductance is:
M = mu_0 * 2*l*[ ln[(l/d)+ sqrt{1 + (l^2/d^2) -{sqrt[1 + [d^2/l^2]] + d/l}
mu _{0}= 4π × 10−7 Comment:N·A−2 (Permeability of free space)
This formula can be obtained from:
Professor Marc Anderson: http://www.thompsonrd.com/induct2.pdf
Frederic W. Grover, Inductance Calculations, Dover Publications.
where l = length of the parallel wires, and d is the separation between the wires.
Here, we are assuming that both the parallel wires are of the same length.
In the problem above, d = R.
The current = 10 Amperes. Since the problem states, it is AC,
we are going to assume it is sinusoidal and 60 hz.
The voltage induced between terminals 1 and 2 of conductor A is:
v = M di/dt volts.
The instantaneous current in conductor B is:
i = IMax sin(wt), where, w = 2*pi.f, f in hz, and t in seconds.
di/dt = IMax wcos(wt)
f =60 in the United States.
IMax = sqrt(2) *10
di/dt = sqrt(2) * 10 *2.0*pi*60* cos(wt)
The procedure we are going to adopt is to calculate
the peak voltage first and then attach the cos(wt) to it.
"""
import math
The Maximum value of I_prime = di/dt = math.sqrt(2)*10.0 *2.0*math.pi*60.0
I_prime_max = math.sqrt(2)*10.0 *2.0*math.pi*60.0
print(I_prime_max)
I_prime_max = 5331.459525790039 Amps = Approximately 5331.46 Amps
Let us calculate the mutual inductance M:
Since no values are given for L and D,
the induced voltage between terminals 1 and 2 is :
= M* 5331.459525790039* cos(wt),
where M is the value of the mutual inductance given by M above.
To attach some numerical values, let the length of the wires = 1 meter,
the distance of separation be = 0.5 meters.
M = mu_0*2*l*[ ln[(l/d)+ sqrt{1 + (l^2/d^2) -{sqrt[1 + [d^2/l^2]] + d/l}
mu_0 = 4* math.pi*10^(-7)
^ stands for exponentiation. * stands for multiplication.
l = 1.0
d = 0.5
a = l/d
print("a = ", a)
b = d/l
print("b =", b)
M = mu_0*2.0* l *[math.log[a1 + math.sqrt[1 + (a1)^2]] - math.sqrt[1 + (a2)^2] + a2]
A = math.log(a + math.sqrt(1 + a^2))
print("A = ", A)
B = math.sqrt(1 + b^2)
print("B = ", B)
M = mu_0*(2.0 lA - B + b)
print(M, 'Henrys')
M = 2.851607267136502e-06 Henrys
V_peak = M * 5331.46
print("The peak voltage between points 1 and 2 =",V_peak )
print("The RMS Voltage between points 1 and 2 =" , V_peak/math.sqrt(2), "Volts")
The peak voltage between points 1 and 2 = 0.015203230080447576
The RMS Voltage between points 1 and 2 = 0.010750307085823781 Volts
or, the RMS(Root Mean Square) Voltage between points 1 and 2 = 10.75 milli-volts.