The question is about why are motorcycles not manufactured with handlebars that can turn to great degrees like a bicycle. In most motorcycles, you hardly have a steering angle of about 20-30 degrees, whereas on a bicycle, you can even go beyond 90 degrees. Is this done with the purpose of stability in mind, as motorcycles travel at far higher speeds than a bicycle, and sudden steering of the vehicle at such speeds can cause it to flip over. Why is this not done at least for motorcycles belonging to the 'streetbike' or 'naked' category, as they are meant to be ridden in cities, at least theoretically, where you might need to take tight turns.
4 Answers
The simplest answer to the question is "because the motorcycle gets in its own way"
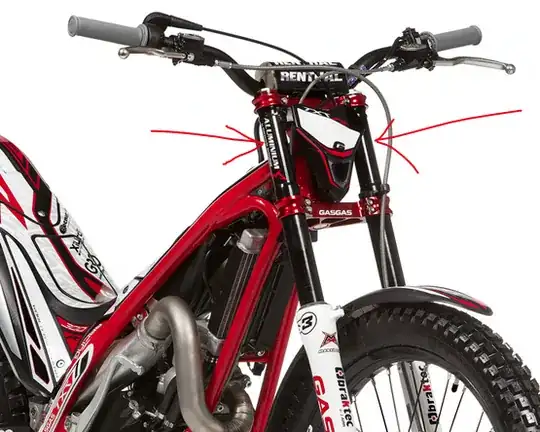
Take a look at this picture of a trials motorcycle; it has perhaps the smallest of turning circles available in a motorcycle of a given length:
And here's a picture of a typical bicycle steering/suspension setup:
On a motorcycle, it's fairly universal to have the suspension arms anchored in yokes in two places (the red clamps around the black tubes are part of the yoke - there is a yoke at the top, near the handlebars and another underneath, near the tire) for reasons of strength. In a bicycle it's common to have the suspension forks anchored in a single yoke underneath the frame tube in which it rotates. This means the steering can spin all the way round, 360 degrees, if it needs to (and other incidentals like cables aren't attached)
You can cast off the cables, or route them through the steering tube but you still won't evade this simple principle; the frame of the motorcycle gets in the way of the suspension tube and limits how much it can rotate.
Exceptions exist; this is a downhill bicycle:
It adopts the motorcycle style of suspension anchoring for reasons of strength, considering the use - high speed, heavy impact. You'll be able to swing these handlebars quite far too; the suspention tubes and frame are slim, but it won't spin 360 degrees.
This is a child's trials motorcycle:
Basically a bicycle with an electric motor; this machine certainly won't be suffering anywhere near the stress that a typical motorcycle would - you won't be doing 100mph on it and need to hit the brakes suddenly and hard, or be landing after a huge jump in a motocross race and be loading several hundred pounds of weight onto the front wheel.
For the stresses most motorcycle front suspension is subjected to you need that double anchor of above and below, and generally the bigger and heavier the motorcycle, the bigger all that componentry is going to need to be.. and the bigger it gets, the less far you can swing it before it bangs into something else. Notice how, as the components get bigger and more heavy duty because the bikes get heavier, the forks also have to be set further and further apart and more forwards, just to keep allowing a reasonable range of swing:
Side note; anything can be designed for any purpose. The owner of this machine clearly felt being able to turn on a dime was important and snapping the suspension in normal use unlikely:
..but by and large engineering anything in this world is about achieving an ideal set of compromises for the task at hand and motorcycles and bicycles have rather different tasks at hand, different sets of physical stresses in operation and are thus engineered appropriately. The difference you've identified is a consequence of that and saying "they should be able to..." does also omit all the other things the "should" be able to do too (not snap when a 200 pound rider doing 60mph grabs the front brake but runs into a hole in the road anyway).
Is this done with the purpose of stability in mind
Unlikely to be the primary consideration. How two wheeled vehicles steer at speed isn't really a factor here. The process for steering at a constant speed is:
- When you want to turn right you (subconsciously) turn the steering to the left slightly
- This causes the -cycle to start to fall over to the right
- As the cyle falls over rightwards, you can then start turning the steering to the right to "catch it" - turning the steering to the right causes a -cycle to "fall over to the left"
- If your -cycle is "already falling to the right" then this "steer to the right to cause the cycle to fall over to the left" means you can counteract the "falling over to the right" with some amount of "falling over to the left"
- This means you can adopt a stable "describing a right hand arc" position where the amounts of "falling to the right" and "falling to the left" are balanced, the cycle is leaned over, it's steering is set pointing slightly right and it is not falling either left or right but is describing a right hand arc
- You continue leaning into the direction of turn without falling off to the left or right of the cycle
- If you need to turn more sharply to the right, you need to make the -cycle fall more to the right, so you actually again steer it a bit left, to induce a rightwards-fall, then as it falls you can feed in more and more "turn to the right" to achieve another balanced set of forces where you're leaned over more, you're describing a sharper turn, more centripetal force is trying to push the -cycle over to the left, more lean/gravity is trying to push the bike over to the right
- When you want to straighten up out of a right turn you actually turn more to the right, which pushes the bike "over to the left" harder, causing you to become more upright. You can then, as you come upright, start feeding in turning the steering leftwards (back to being straight).
- If you were leaned over to the right, in stable configuation, then turned more to the right and kept it that way you would very soon be thrown off the -cycle as it violently picks itself upright and then over to the left.
- If you were leaned over to the right, in stable configuation, but your steering is turned all the way to the right and banging into the frame of the cycle you wouldn't be able to pick it upright from steering alone because you can't turn any more to the right to initiate a "fall over to the left"; you'd have to accelerate to cause an increase in centripetal force which would push the cycle upright
One of the most significant skills in riding larger motorcycles at speed and flicking them between upright and leaned-over for fast, sharp corners is knowing exactly how much opposite steer to apply to cause the bike to quickly fall over to a lean angle that will go round the corner, and then how to quickly apply same-direction steer to get to a point where the falling over is halted, the bike goes round the corner and then the reverse operation picks the cycle upright again
Critically, none of this steering operation needs anywhere near 90 degrees of turn; the faster you go, the less you need. To a huge extent steering a cycle is not just about "pointing the front wheel in the same direction as the corner" - it is absolutely vital that the steering is also used to make the cycle fall over and your brain is doing a constant balancing act between the current speed, the rate of acceleration or deceleration (slower speeds need greater turns on the steering to cause a "falling over" in one direction or another), the amount of "fall to the left/right" and how much the steering is turned.
where you might need to take tight turns
If you have a cycle that can turn 90 degrees, and it is the rear wheel that is driven, you can achieve a scenario where the front wheel is turned 90 degrees and becomes a perfect brake for the motion of the cycle. There's no overall force that will encourage the front wheel to rotate one way or the other and indeed as a front wheel is turned more and more toward 90 degrees the force that must be applied by the back wheel to get things moving at all is greater and greater. A cycle with a wheel turned 90 degrees doesn't steer at all.
If the front wheel were driven, it wouldn't matter; the front wheel would easily rotate even at 90 degrees and the bike would pivot round its back wheel- the smallest turning circle it can achieve without travelling slightly backwards at the same time. You can achieve this with a cycle that only has a relatively small amount of steering angle by lying it down more, so that the contact point the front wheel makes with the floor reaches the point of the tire that is level with the axle when the wheel is upright. So long as you can turn a motorcycle steering far enough to the right that the frontmost point of the wheel is toughing the floor and nothing else is, you can drag that cycle round in a very tight turn. Of course you're using your body strength to counteract gravity and you're pulling it sideways to rotate the front wheel but it's a balanced set of forces achieving a turn all the same. In "normal operation" of a cycle though the balanced set of forces come from a different arrangement, so we get back towards that "because there's a set of compromises that must be met across all environments so that is what we do" which ultimately leads to an answer of "motorcycles don't turn as sharply as bicycles because they dont need to". You'll never try to flip one round in your hallway (tip for bicycle; don't steer to do that either - put the back brake on, walk backwards, then spin it round on its back tire and put it down)
- 301
- 1
- 4
A bicycle usually weights about 18 pounds versus an average of 180 pounds for a motorcycle.
In tight turns a bicycle can easily be controlled by the rider shifting their body's center of mass as needed to nudge the bicycle to turn or correct extra overturning moments, by leaning in or out of the turn while playing with the handle bar.
The weight of front wheel and handles are so light that one can rapidly try correcting over-steering or even keep the bicycle on a perpetual dance back an forth around a small pivot.
In a motorcycle even if the geometry of the handles allow a great flexibility, maintaining stability of such a tight turn by just leaning in or out of a overly tilting motorcycle is impossible, because of the ratio of the weight of the rider to the bike.
Motorcycle turns require a greater radius and faster speed to provide sufficient centripetal force to counter the great overturning moment of a slanted motorcycle.
The correction for oversteering is done by gently adding power or gently braking, both having a long period of delayed response after applying the correction.
The heavier the bike the larger turning radius.
I'll approach this from a different perspective to the other answers: Pushbikes have no limits on the steering range because they don't need to add the complexity and weight. They're simple, light, and traditional, so include only the features necessary. Turning the bars more than a few degrees while riding along at any decent speed isn't needed, bu it may be at very low speeds or when parking (which may be done in much tighter spaces than motorbikes, and by pushing). I tried to eyeball this on my commute last night. That's never easy with angles, let alone when looking out for traffic, but at road speeds (roughly 20km/h or 15mph) the bars only moved by a couple of degrees, and 10--15° max at a slow walking pace to get from the bike parking to the road.
Most bikes will have their steering limited by the range of movement of brake/gear cables (or brake hoses), or by the handlebars coming into contact with the toptube, or something like that (in my case, often bars vs. luggage, perhaps mounted where a motorbike's fuel tank would be). There are typically 4 Bowden cables/hoses and possibly one or two lighting power cables to couple between the forks and the frame. The electrical connections, if present, may wear from handlebar movement but are unlikely to suffer catastrophic failures; the mechanical and hydraulic connections are far tougher and will wear from use much faster than from turning the bars.
On a motorbike there are more control lines and critical electrical cables running to the bars, and these are bigger, stiffer, but not really any stronger, so they need protecting, both by restricting the movement and by sheathing them in ways that work better when restricted. Failure modes are likely to be more severe as well. Fairings (when present) on frame and forks have to be designed not to contact each other unexpectedly while doing their job with respect to airflow. Limiting the range of movement helps the designer here. The combination of fairings and far more controls on the handlebars means it would be harder to design a motorbike so everything was sensibly located, but the bars couldn't hit the tank for a large movement.
Note that it is possible to retrofit steering dampers to pedal bikes, which also limit the steering range. In the same way, bikes often aren't supplied with kickstands, but they may be retrofitted.
- 398
- 1
- 6
Although there is a correlation between high speed, stability and limited steering range, I think this question is about low velocities. I.e. why even for low velocities, there is still not enough steering range for motorcycles. Therefore, IMHO, the reasoning that at high velocities need larger radii does not by itself prohibit greater steering range at smaller velocities.
1. Loads and strength result in increase stiffness of steering column
IMHO, the main issue is that there are heavy load during the front braking maneuver, and the increased stiffness requirements for the steering column compared to bicycles. The front braking is more efficient due to the greater reaction on the front wheel (greater reaction from the ground). Also, the loads for deceleration on motorbikes are significantly higher due to the high speeds.
Due to the higher compressive load, additional strength of the steering column is required. Most motorcycles (all racing) have a double column in order to increase the second moment of area, and avoid bending/buckling. The double column is limiting the range of movement because of the rest of the frame which is also more robust.
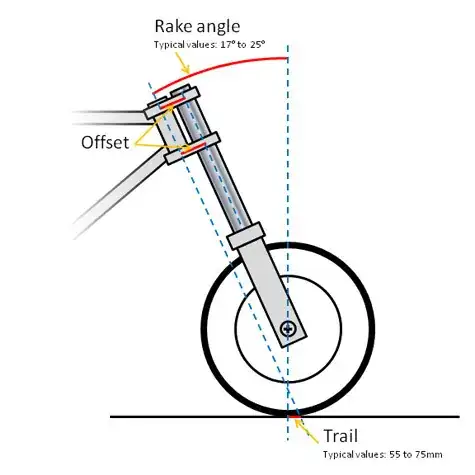
steering wheel in bicycles is more vertical, in motorcycles usually there is a greater rake angle: This provides among other things better stability during braking from overturning during breaking. Typical values for a motorcycle are over 25 degrees, while for bicycles (which is called head angle and its measured differently) are less than 20.
Figure :Rake angle (source bikesmedia)
2. Center of gravity and rake angle.
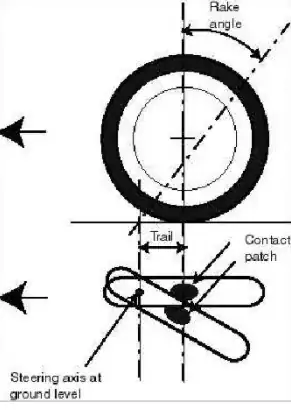
Because of the higher rake angle in motorcycles (see above reasons), when turning the wheel at greater angles the contact patch will be moved outside the original line.
 Figure: effect of turning at 90 degrees the steering wheel. The removed rubber is to simumate the contact patch (I've used a cut extrude) (source: the original XS650 model was from Grabcad)
Figure: effect of turning at 90 degrees the steering wheel. The removed rubber is to simumate the contact patch (I've used a cut extrude) (source: the original XS650 model was from Grabcad)
The problem then is that for heavier motorcycles, a lot of effort is required to keep the bike from falling over. So as a compromise, smaller angles are introduced.
Figure : shift of the contact patch due to rake angle and trail (source: Chaperot, Fyfe)
- 24,340
- 3
- 38
- 77