I've got a box running Win2k3 and some directions from Microsoft KB about SSL certificates, for IIS 5.0 and 6.0. How can I tell which version of IIS is currently installed?
13 Answers
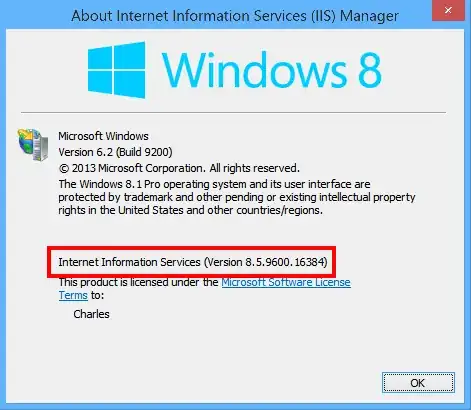
When you have IIS Manager open, you can click Help -> About to see the version.
- 459
- 2,832
As a more general answer, not specifically aimed at your question, Microsoft has a support article which lists all old versions and the operating systems that provide each one.
IIS version Built-in
5.0 Windows 2000
5.1 Windows XP Pro
6.0 Windows Server 2003
7.0 Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008
7.5 Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2
8.0 Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012
Current versions are on Wikipedia
8.5 Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2
10.0 v1607 Windows Server 2016 and Windows 10.*
10.0 v1709 Windows Server 2016 v1709 and Windows 10.*
10.0 v1809 Windows Server 2019 and Windows 10.* October
- 1,856
You can look at %SYSTEMROOT%\system32\inetsrv\inetinfo.exe (or inetmgr.exe or w3wp.exe). Right-click and get properties, click the Version tab.
You can also look at an HTTP response header
- telnet mywebserver 80
- type in HEAD / HTTP/1.0 [enter][enter]
- Look at the line that starts with Server:
Windows XP has IIS 5.1 installed, so use the IIS 5.0 procedure. See this article for an overview of IIS 5.1:
A look at IIS 5.1 in XP Pro - What's different from IIS 5?
IIS 5.1 is a feature only to be found on Microsoft's XP Pro operating system. It is not installable (reliably) on XP Home. Additionally, there are no plans to update IIS 5.0 on Windows 2000 to IIS 5.1.
IIS 5.1 is basically the same engine as IIS 5.0 but since XP is a client operating system, it has the built in limits that are customary for Microsoft’s client operating systems—such as connection limits and only one Web site. Even though based on IIS 5, there are significant differences from IIS 5.0 that you should know about.
You could also open a page in the browser which runs this simple asp Script:
<%
response.write(Request.ServerVariables("SERVER_SOFTWARE"))
%>
As a side note: it is interesting that IIS (beginning with Windows Server 2000/version 5.0) can't be upgraded without upgrading the operating system. Every Windows version has it's own IIS version:
Windows NT 3.51 1.0 Windows NT 4 2.0-4.0 Windows Server 2000 5.0 Windows XP Professional 5.1 Windows Server 2003 6.0 Windows Vista 7.0 Windows Server 2008 7.0 Windows Server 2008 R2 7.5 Windows 7 7.5 Windows Server 2012 8.0 Windows 8 8.0 Windows Server 2012 R2 8.5 Windows 8.1 8.5 Windows Server 2019 10.0
You should be able to determine the IIS version number from the following registry value: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\InetStp\VersionString
This shows "Version 6.0" on my local machine.
reg.exe query HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\InetStp /v VersionString
- 117
Here, the updated version table to Windows 10 and Windows Server 2016:
IIS 1.0 Windows NT 3.51
IIS 2.0 Windows NT 4.0
IIS 3.0 Windows NT 4.0 SP3
IIS 4.0 Windows NT 4.0 Option Pack
IIS 5.0 Windows 2000
IIS 5.1 Windows XP Professional x32
IIS 6.0 Windows Server 2003
IIS 6.0 Windows Server 2003 R2
IIS 6.0 Windows XP Professional x64
IIS 7.0 Windows Server 2008 / Windows Vista
IIS 7.5 Windows Server 2008 R2 / Windows 7
IIS 8.0 Windows Server 2012 / Windows 8
IIS 8.5 Windows Server 2012 R2 / Windows 8.1
IIS 10.0 Windows Server 2016 / 2019 / Windows 10
And other methods would be:
Properties on the file: InetMgr.exe via GUI, or via PowerShell:
[System.Diagnostics.FileVersionInfo]::GetVersionInfo("$env:SystemRoot\system32\inetsrv\InetMgr.exe").ProductVersion
Extracted from: http://www.sysadmit.com/2017/05/windows-iis-como-saber-la-version-instalada.html
- 513
If you have curl and grep installed, e.g. through Cygwin, or from another machine running OS X or Linux, you can use the power of command line tools and avoid knowing where exactly to click in which situation:
$ curl --silent -I http://microsoft.com/ |grep Server
Server: Microsoft-IIS/8.5
Note there is no requirement to be on the server itself.
Also note: this only works if the application and/or server configuration does not set an alternate header. Often application developers or system administrators will turn off this header or set it to some other value in order to prevent attackers from seeing it - a form of security by obscurity.
- 3,261
- 468
- 8
- 23
Just as a fun data point:
From 32-bit land:
Windows XP ships with IIS 5.1.
Windows Server 2003 with IIS 6.0.
But the x64 edition of Windows XP is based on the Windows Server 2003 SP1 codebase, and the version of IIS included in Windows XP Professional X64 Edition is IIS 6.0.
Crazy stuff, I know.
- 9,173
- 2
- 30
- 39
Use PowerShell from the command line, like this
powershell "get-itemproperty HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\InetStp\ | select setupstring,versionstring"
- 133
If you have no access what so ever to the back end of a machine you can try using NetCraft such as http://toolbar.netcraft.com/site_report?url=http://www.starbucks.com
There are enough little finger prints on the headers the machine gives off, that they can usually identify the signature of the machine, unless someone alters them on purpose.
- 111
You can also run this PowerShell script:
$w3wpPath = $Env:WinDir + "\System32\inetsrv\w3wp.exe"
$productProperty = Get-ItemProperty -Path $w3wpPath
Write-Host $productProperty.VersionInfo.ProductVersion
Source: https://gallery.technet.microsoft.com/how-to-obtain-versions-of-7875ac84
- 129
Very simple to know the IIS Version installed on your system.
Simple type localhost on your browser and enter you are able to see the IIS version.