I checked /var/log and /usr/local/mysql and i can't seem to find the log. I am trying to troubleshoot an error establishing a database connection with a php function.
11 Answers
As Chealion mentioned, there are several ways that your mysql could have been installed. Each of which will place your data dir and/or logs in different locations. The following command will give you (and us) a good indication of where to look.
ps auxww|grep [m]ysqld
# Putting brackets around the first char is a `grep`+`ps` trick
# to keep it from matching its own process.
# Note: For zsh compatibility put quotes around the grep regex
Can you post the result of that command here please? Mine looks like this:
_mysql 101 0.0 0.3 112104 13268 ?? S 12:30AM 0:13.20 /opt/local/libexec/mysqld --basedir=/opt/local --datadir=/opt/local/var/db/mysql --user=mysql --pid-file=/opt/local/var/db/mysql/rbronosky-mbp.pid
root 76 0.0 0.0 600172 688 ?? S 12:30AM 0:00.02 /bin/sh /opt/local/lib/mysql/bin/mysqld_safe --datadir=/opt/local/var/db/mysql --pid-file=/opt/local/var/db/mysql/rbronosky-mbp.pid
From that you can see that my datadir is /opt/local/var/db/mysql (because I installed via MacPorts). Let's take this lesson a bit further...
From the first line you can see the my daemon is /opt/local/libexec/mysqld. The mysqld can be called with --verbose --help to get a list of all command line options (and here is the important/valuable part!) followed by the values that would be used if you were launching mysqld instead of just checking the help output. The values are the result of your compile time configuration, my.cnf file, and any command line options. I can exploit this feature to find out EXACTLY where my log files are, like so:
/opt/local/libexec/mysqld --verbose --help|grep '^log'
Mine looks like this:
log /tmp/mysql.log
log-bin /tmp/mysql-bin
log-bin-index (No default value)
log-bin-trust-function-creators FALSE
log-bin-trust-routine-creators FALSE
log-error /tmp/mysql.error.log
log-isam myisam.log
log-queries-not-using-indexes FALSE
log-short-format FALSE
log-slave-updates FALSE
log-slow-admin-statements FALSE
log-slow-queries (No default value)
log-tc tc.log
log-tc-size 24576
log-update (No default value)
log-warnings 1
LO AND BEHOLD! all of the advice in the world was not going to help me because my log file is kept in a completely non-standard location! I keep mine in /tmp/ because on my laptop, I don't care (actually I prefer) to loose all of my logs on reboot.
Let's put it all together and make you a oneliner:
$(ps auxww|sed -n '/sed -n/d;/mysqld /{s/.* \([^ ]*mysqld\) .*/\1/;p;}') --verbose --help|grep '^log'
Execute that one command and you will get a list of all of the logs for your running instance of mysql.
Enjoy!
This Bash-Fu brought to you for free by my commitment to all things Open Source.
- 4,599
There are 3 types of MySQL/MariaDB logs:
log_errorfor the error message log;general_log_filefor the general query log file (if enabled bygeneral_log);slow_query_log_filefor the slow query log file (if enabled byslow_query_log);
Check the settings and location of above logs by this shell command:
mysql -se "SHOW VARIABLES" | grep -e log_error -e general_log -e slow_query_log
By default the logs are stored in your data dir, so check location by this shell command:
mysql -se "SELECT @@datadir"
To view your error log, you can run:
sudo tail -f $(mysql -Nse "SELECT @@log_error")
If you've general log enabled, to view it, run:
sudo tail -f $(mysql -Nse "SELECT CONCAT(@@datadir, @@general_log_file)")
- 7,125
Another way to find this information is to use lsof.
Use Activity Monitor to find the PID of
mysql, or useps -ef | grep mysqldto find it.sudo lsof -p PID_OF_MYSQLDand see which files MySQL has open.
- 6,671
Took myself a while to find this... try this location:'
sudo vi /usr/local/mysql/data/YOUR-USERNAME.local.err
By default, all log files are created in the mysqld data directory.
Source: MySQL Documentation
You can use mysqlbinlog to read the binary log files in /usr/local/mysql/data/ (in my installation not all were binary). Some errors are simply directed to stderr so you may want to check /var/log/system.log as well.
- 5,753
- Open System Preferences
- Select MySQL -> Configuration
Your Path to Error Log should be visible:
- 1
Try to locate your mysql (or mariadb) log folder by this command:
locate local.err
- 101
The approved answer from Bruno didn't work for me on MacOS Monterey, and in any case, it won't help you if your problem is that there is no mysqld process because it failed during startup.
However, following some of the others here enabled me to find the error log:
$ ls -l /usr/local/mysql
lrwxr-xr-x 1 root wheel 26 18 Jul 13:39 /usr/local/mysql -> mysql-8.0.29-macos12-arm64
$ sudo ls -l /usr/local/mysql-8.0.29-macos12-arm64/data|grep err
-rw-r----- 1 _mysql _mysql 3308 18 Jul 15:01 mysqld.local.err
- 111
The folder holding that log may not be accessible to you without using sudo:
sudo ls -l "/usr/local/mysql-5.0.51a-osx10.5-x86"
[..]
drwxr-x--- 4 _mysql wheel 136 Jul 10 23:06 data
If you happen to find a large log file and when you're using Time Machine, you may want to read What is Time Machine doing? on Server Fault.
By default, all log files are created in the mysqld data directory. Unfortunately, many people don't put their log files (and programs) in their typical locations. I'm one of them!
I went through this routine myself with MySQL until I tried out Navicat for MySQL. Later I upgraded to Navicat Premium. Both have a Monitoring tool that contains a tab with all of the server variables in one comprehensive list. Here's a screenshot with the log_error server variable:
log_error server variable in Navicat Server Monitoring Tool
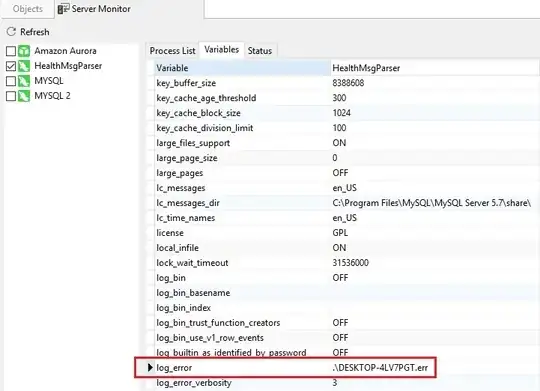
You can also set the variables right there in the list.
Cheers!
- 1,086
- 101