I am doing a lot of sequence diagrams. We decided to start at a subsystem level of abstraction because we do not have all the details yet. In my diagrams I was using this definition of Actor:
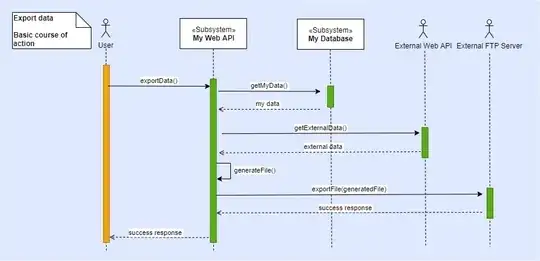
So the resulting diagram of a hypothetical system that exports data would be:
Notice that External Web API and External FTP Server are considered actors because they exist even if my system doesn't.
A friend of mine told me that he thinks that Actors are initiators of interactions like User and they don't wait passively to be invoked.
On the other hand, the acording to UML standard an Actor:
specifies a role played by a user or any other system that interacts with the subject
and
Actors may represent roles played by human users, external hardware, or other subjects ...
I think that External Web API meets at least these two requirements. Even though it doesn't initiate the interaction, it interacts with my system by responding the call made by My Web Api.
So, should I represent it as an Actor or just as another Subsystem?