I am currently trying to follow the clean architecture approach but i wonder where common things like a database connections should take place.
Right here:
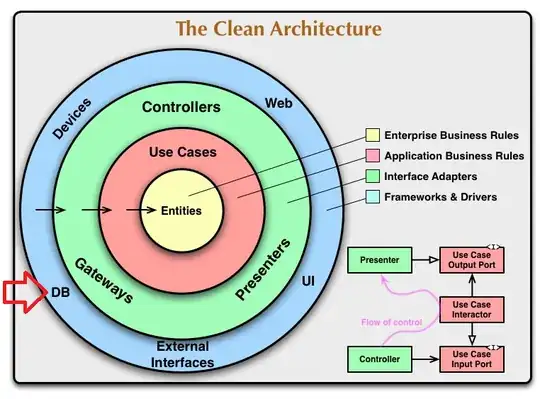
Since i think a database connection usually will be opened once, but different tables in there are used from feature to feature in different ways, it wouldn't make much sense to implement (even as a singleton pattern) for this in every feature that will be developed.
A "feature" isn't an architectural thing in Clean Architecture. Sorry but it just isn't. The closest Clean comes is the use case. Package by feature is a good idea. It's just someone else's idea.
That said, you can be feature centric and still use Clean Architecture. Heck, each feature can have it's own onion.
But the almost every example (at least for my current flutter application) i found is exactly doing this. The database instance is being created in a feature itself.
Which is fine. But it's also not something Clean Architecture speaks to. Clean Architecture is a dependency diagram. It shows you what statically knows about what. It doesn't show you how to build it. Just what it should look like when you're done.
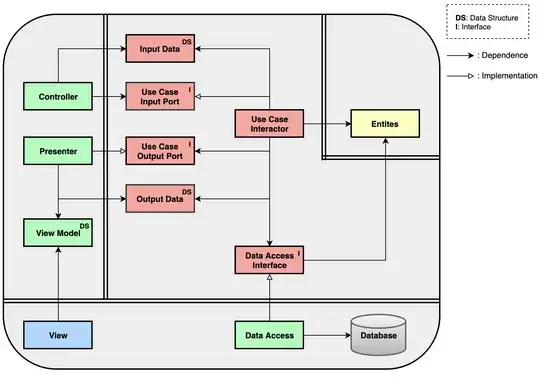 github.com - esakik
github.com - esakik
Can you look at that and tell me if Data Access is a long lived object that was built in main() (Who needs singletons?) or something that the Use Case Interactor had built just now? Nothing in these diagrams answers that question. So you're free to do it either way and can still claim you're following Clean Architecture.
Why DB is then put on the outer circle when it should be accessible from the entities? Jim Panse

The DB is accessible from the entities. Remember, this is a dependency diagram.= Not a data flow diagram.== Those black arrows going into the circles don't mean this is a roach motel that traps you inside.
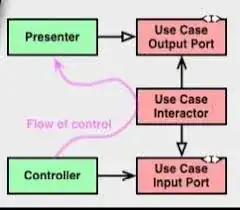
Uncle Bob tried to make that clear with the little "Flow of control" diagram in the lower right corner. Notice Presenters dependency arrow points to Use Case Output Port but the Flow of control goes exactly the other way. That's what they call dependency inversion.== Because of that, control can dive into a lower layer and come back out. All without using return!
And if you can do that, you can do this:
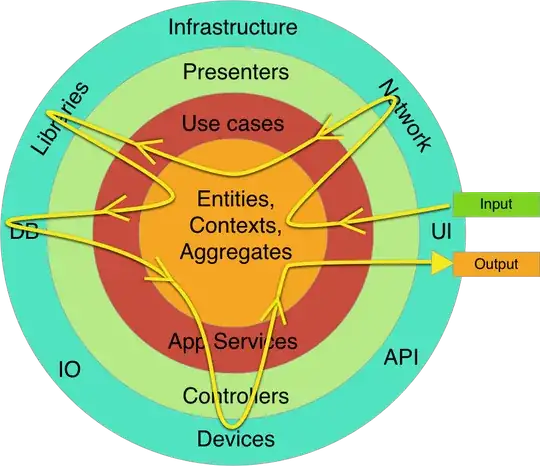 crosp.net
crosp.net
So don't feel like you have to do this:
 slideshare.net
slideshare.net
youtube.com - The Principles of Clean Architecture by Uncle Bob Martin
By the way, Casey Muratori is a game dev with a focus on performance who has been critical of some of Uncle Bobs teachings. You can see them hash it out here. It's a really good read and a good reminder that doing stuff this way isn't free.





